5G Fixed Wireless Internet and Satellite Internet
- (How Data Moves Through A Satellite Network - GroundControl)
- Overview
Fixed wireless internet transmits signals from local towers to a receiver at your home, while satellite internet sends signals between your home dish and an orbiting satellite.
Fixed wireless typically has lower latency and is less affected by weather, making it better for real-time applications like online gaming, but requires a clear line of sight to a tower.
Satellite internet can be installed virtually anywhere with a clear view of the sky but suffers from higher latency and can be more affected by bad weather.
The convergence of AI, Quantum, 5G/6G, and Satellite is creating a more secure, intelligent, and ubiquitous global infrastructure, with 5G acting as the catalyst for the intelligent, automated, and hyper-connected economy.
A. Fixed Wireless Internet:
1. How it works: A local ground-based tower sends a signal to a receiver on your home.
2. Pros:
- Lower latency (lag) due to the shorter distance the signal travels, making it better for activities like online gaming and video calls.
- Less susceptible to bad weather like heavy rain or snow.
- Generally more stable performance.
3. Cons:
- Requires a clear line of sight between your home receiver and the tower, often within about 10 miles.
- Availability is limited to areas with the necessary tower infrastructure.
B. Satellite Internet:
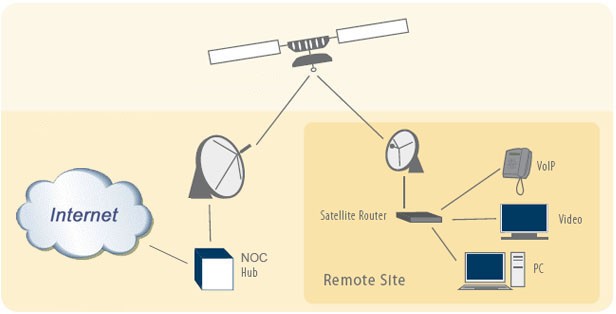
1. How it works: Your home dish communicates with a satellite orbiting the Earth to access the internet.
2. Pros:
- Available almost anywhere, as long as you have an unobstructed view of the sky.
- Can reach very remote or underserved locations where fixed wireless or other wired options are not available.
3. Cons:
- High latency (lag) because the signal must travel a much greater distance to and from the satellite.
- More susceptible to weather interference, as heavy rain, snow, or even cloud cover can disrupt the signal.
- Can be a poor choice for real-time applications like online gaming or video conferencing due to the delay.
- Which to Choose: Fixed Wireless or Satellite
5G Fixed Wireless (FWA) uses nearby cell towers for fast, low-latency internet, great for gaming and streaming, while Satellite uses orbiting satellites, offering coverage almost anywhere but with high latency and weather susceptibility, making 5G generally superior for performance where available, but satellite a crucial option for the most remote areas.
5G offers quicker installation and often better pricing, whereas satellite excels in reaching truly isolated spots with a clear sky view.
A. 5G Fixed Wireless Internet (FWA):
1. How it works: Connects to a 5G cell tower via an antenna/receiver at your home, like a cellular connection but fixed.
2. Pros:
- Speed & Latency: Much faster speeds (hundreds of Mbps to 1 Gbps) and very low latency (under 50ms), ideal for real-time apps.
- Reliability: More stable, less affected by weather than satellite.
- Installation: Simpler, often plug-and-play.
- Cost: Often competitive pricing with unlimited data options.
3. Cons:
- Coverage: Requires good 5G coverage and proximity to a tower (typically 10-20 mile radius).
B. Satellite Internet:
1. How it works: Data travels from your dish to a satellite in orbit and back, a long distance that causes delays.
2. Pros:
- Coverage: Reaches nearly any location with a clear view of the sky, even very remote areas.
3. Cons:
- Latency: High latency (600ms+) makes it poor for gaming, video calls.
- Speed: Generally slower and less consistent than 5G FWA.
- Weather: Signal can degrade significantly in rain, snow, or high winds.
- Installation: Requires precise dish alignment.
C. Which to Choose?
- Choose 5G FWA if: You have good 5G coverage, want faster speeds, lower latency for gaming/streaming, and easier setup.
- Choose Satellite if: You are in a truly remote area with no cellular signal and need any internet connection, accepting performance trade-offs.
- The Integration of AI, Quantum Computing into 5G and Beyond Fixed Wireless Internet and Satellite Internet
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Quantum Computing into 5G, 6G, Fixed Wireless Access (FWA), and Satellite Internet is transforming telecommunications from passive connectivity into intelligent, autonomous, and secure networks.
These technologies are bridging the gap between high-speed terrestrial networks and global, low-latency satellite coverage, with AI optimizing performance and Quantum Computing securing data.
1. AI and Quantum in 5G and Beyond (6G) Networks:
AI is shifting from being "bolted onto" 5G to being a native, foundational component of 6G, enabling self-optimizing, autonomous, and energy-efficient networks.
- AI-Native Networks: Future networks will use AI for real-time, closed-loop automation—managing, configuring, and troubleshooting themselves without human intervention.
- Network Optimization: AI techniques like Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) are used for traffic forecasting, dynamic resource allocation, and beamforming in Massive MIMO systems, reducing latency and boosting efficiency.
- Quantum-Enhanced AI: Quantum algorithms are emerging to process complex, multi-parameter optimizations in 6G and THz communications that are too computationally expensive for classical AI.
- Security: As quantum computers threaten current encryption, Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) and Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) are being deployed to secure 5G/6G infrastructure.
2. AI in Fixed Wireless Internet (FWA):
5G-powered FWA is becoming a primary broadband solution, with AI enhancing performance at the edge.
- Intelligent CPE: AI-integrated 5G modem chips allow Customer Premises Equipment (CPE) to perform real-time, self-healing, and diagnostic optimization.
- Enhanced Performance: AI improves spectral efficiency by ~40% and reduces energy consumption by ~25%, while predicting, rather than reacting to, congestion.
- Smart Home Integration: AI-powered 5G CPE serves as a hub for smart home ecosystems, managing security, environmental inputs, and user behavior.
3. AI and Quantum in Satellite Internet:
Satellite internet, particularly Low-Earth Orbit (LEO) constellations, is leveraging these technologies to enhance reliability and security.
- Satellite-Based QKD: China’s Micius and other European initiatives (Eagle-1) are using satellites to transmit unbreakable encryption keys to ground stations.
- Uplink Technology Breakthrough: Researchers have proven that an Earth-to-space quantum link is feasible, where photons are generated on Earth and sent up, enabling high-bandwidth, secure quantum networking.
- Optimized Resource Allocation: Quantum computing enhances satellite bandwidth utilization, ensuring reliable communication in remote and underserved areas.
- AI-Powered Satellite Operations: AI is being applied to optimize satellite constellations (in-orbit servicing), manage laser communications, and improve space situational awareness (SSA).
4. Future Outlook and Challenges:
- 6G Transformation: By 2030–2035, 6G will deliver terabit-level speeds and near-zero latency, powered by AI that manages Everything-as-a-Service.
- Hybrid Networks: The next decade will see hybrid classical-quantum systems, with 5G/6G and satellite networks integrating to create a "quantum internet".
- Challenges: Key hurdles include the 10–15 year timeline for fault-tolerant quantum computers, high energy consumption of AI, and the need for standardized, interoperable protocols.
[More to come ...]