Distributed Cloud Edge Computing
- Overview
Distributed cloud edge computing combines the concepts of distributed cloud and edge computing to enable processing closer to the data source while maintaining centralized management.
This approach leverages multiple cloud resources across different locations, including customer premises, third-party data centers, and public cloud regions, all managed from a single control plane. This allows for reduced latency, improved performance, and enhanced security, especially for applications requiring real-time data processing.
The concept of distributed cloud is also relevant to edge computing. This means that a single cloud provider manages resources across multiple locations, offering a consistent experience while distributing processing power.
Edge computing is not meant to replace the cloud, but rather to complement it. The cloud still handles large-scale data processing and storage, while the edge handles real-time, localized processing needs.
1. Edge Computing:
- Focus: Bringing computing resources and data storage closer to the devices and users generating data.
- Goal: Reduce latency, improve responsiveness, and enable real-time data processing.
- Example: Processing sensor data from a manufacturing plant on-site instead of sending it to a distant data center.
2. Distributed Cloud:
- Focus: Distributing cloud resources across multiple locations, including on-premises, edge, and public cloud environments.
- Goal: Enhance performance, meet regulatory requirements, and support edge computing initiatives.
- Example: A public cloud provider offering services in multiple regions and customer data centers.
3. Distributed Cloud Edge Computing:
- Concept: Combines the benefits of both edge and distributed cloud architectures.
- How it works: A public cloud provider's infrastructure is extended to edge locations (on-premises, third-party data centers, etc.), allowing for centralized management of resources across all locations.
Benefits:
- Reduced latency: Processing data closer to the source minimizes delays.
- Improved performance: Faster response times for time-sensitive applications.
- Enhanced security: Data can be processed locally, minimizing the need to transmit sensitive information to a central location.
- Scalability and flexibility: Resources can be dynamically allocated and managed across various locations.
- Compliance: Data residency and other regulatory requirements can be more easily met.
4. Use Cases:
- 5G networks: Deploying 5G core and radio access network (RAN) elements at the edge to support enhanced mobile broadband and low-latency applications.
- Industrial IoT: Enabling real-time monitoring and control of industrial equipment and processes.
- Automotive: Supporting connected car applications, such as autonomous driving and real-time traffic updates.
- Healthcare: Enabling remote patient monitoring, telehealth services, and faster access to patient data.
- Retail: Facilitating personalized shopping experiences, inventory management, and loss prevention.
- Distributed Cloud Computing
Distributed cloud refers to a cloud computing model where a single public cloud provider manages multiple geographically dispersed cloud deployments. This allows organizations to meet specific needs like regulatory compliance, performance requirements, and edge computing demands while maintaining a centralized management and control plane. Essentially, it's a way to extend the reach and capabilities of a public cloud while keeping management relatively simple.
This model combines the benefits of public cloud (scalability, cost-effectiveness) with the advantages of geographically distributed infrastructure (reduced latency, improved performance, enhanced compliance).
1. Key aspects of distributed cloud:
- Decentralized Infrastructure: Cloud services are physically located closer to users and data sources, enabling faster processing and reduced latency.
- Centralized Management: Despite the distributed infrastructure, the cloud provider manages and operates the services, ensuring consistency and ease of use.
- Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Support: Distributed cloud can be implemented in hybrid and multi-cloud environments, allowing organizations to leverage resources from different providers.
- Edge Computing Integration: Distributed cloud can extend cloud capabilities to the edge of the network, bringing processing power closer to devices and users.
2. Benefits of distributed cloud:
- Reduced Latency: By distributing resources closer to users, distributed cloud minimizes the time it takes for data to travel, resulting in faster response times for applications and services.
- Improved Performance: Distributed cloud can handle large amounts of data and traffic more efficiently due to the geographically dispersed infrastructure.
- Enhanced Compliance: Distributed cloud can help organizations comply with data residency regulations by keeping data within specific geographic regions.
- Increased Flexibility and Scalability: Organizations can scale their cloud resources up or down as needed, without being limited by a single physical location.
- Cost Optimization: Distributed cloud can optimize costs by leveraging resources in different locations based on demand and usage patterns.
3. Examples of distributed cloud applications:
- IoT Networks and Machine Learning: Distributed cloud enables real-time processing of data generated by IoT devices and facilitates machine learning applications that require low latency.
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): Distributed cloud can power CDNs, improving the performance of websites and applications by caching content closer to users.
- Gaming and Streaming: Distributed cloud can reduce latency for online gaming and streaming services by bringing infrastructure closer to players and viewers.
- Healthcare: Distributed cloud can support applications that require low latency and data residency, such as remote patient monitoring and medical imaging.
- Edge Computing as a Distributed Cloud
Edge computing can be seen as a form of distributed cloud, where computing resources are located closer to the data source, rather than in centralized data centers.
This distributed nature brings processing closer to devices like IoT sensors and mobile devices, enabling faster response times, reduced latency, and lower bandwidth consumption.
1. Concept:
- Distributed Cloud: Edge computing leverages a distributed cloud architecture, meaning that computing power is spread across multiple locations rather than being concentrated in a single central cloud.
- Proximity to Data: Edge computing moves processing closer to the data sources (e.g., IoT devices, sensors, mobile devices). This contrasts with traditional cloud computing, where data is often sent to remote data centers for processing.
2. Benefits of Proximity:
This proximity offers several benefits:
- Reduced Latency: Faster response times are achieved because data doesn't have to travel as far to be processed.
- Lower Bandwidth Consumption: Less data needs to be transmitted over the network, as some processing happens locally.
- Improved Reliability: In some cases, edge computing can maintain functionality even when the connection to the central cloud is unavailable.
3. Examples: Examples of edge computing applications include:
- IoT devices: Processing data from sensors in smart homes, factories, or smart cities closer to the devices.
- Autonomous vehicles: Performing real-time processing for navigation and safety systems.
- Augmented reality: Providing low-latency experiences for AR applications.
- Content delivery: Caching frequently accessed content closer to users for faster delivery.
4. Security:
- Edge computing introduces unique security considerations due to the distributed nature and potential vulnerabilities of edge devices. Security measures like encryption and secure boot are crucial.
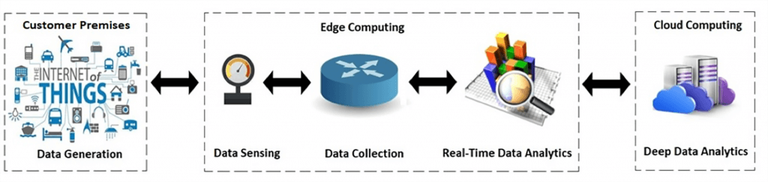
- Edge-Cloud Architecture in Distributed System
For more than a decade, centralized cloud computing has been considered the standard IT delivery platform. Despite its ubiquity, emerging needs and workloads have exposed its limitations.
Some cloud service providers have thought hard about how to support resource-constrained nodes that can only be accessed through unreliable or bandwidth-limited network connections, or how to meet the needs of applications that require extremely high bandwidth, low latency, or widespread computing power across multiple sites.
New applications, services, and workloads increasingly require a different type of architecture, one that can directly support distributed infrastructure. To meet current needs (retail data analytics, web services) and future innovations (smart cities, AR/VR), remote site availability and cloud capabilities need to meet new requirements.
To cope with changing needs, the maturity, robustness, flexibility, and simplicity of the cloud now need to extend to multiple sites and networks. Edge computing is a distributed computing model in which computing occurs near the physical location where data is collected and analyzed, rather than on a centralized server or cloud.
This new infrastructure includes sensors to collect data and edge servers to process data securely in real time on site, while also connecting other devices such as laptops and smartphones to the network.
Edge computing solutions facilitate data processing at the source of business data, thereby reducing the steps required to process data, thereby improving workflow efficiency.
Edge computing is a major driver and key enabler of digital transformation projects. One of the guiding principles behind digital transformation initiatives is to improve the efficiency of business workflows.
Any additional data processing steps and any delays in the processing of digital inputs can have a negative impact. The surge in business inputs from new sources such as IoT devices further exacerbates this challenge.
Typically, data centers have a high-speed, ultra-low latency centralized core. But this capability needs to be distributed to the edge of the network for technologies such as 5G/6G to truly take off.
Deploying capabilities at the edge is the only way to provide low-latency support for applications such as autonomous vehicles, high-frequency trading, or mobile VR. Distributed edge computing infrastructure is key to mobile 5G/6G.
[More to come ...]