Digital Currency and Lending
- Overview
Digital Currency and Lending is a broad term encompassing the borrowing and lending of digital money, including Cryptocurrencies and Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs). It can involve using cryptocurrency as collateral for a cash loan (crypto lending) or using digital platforms for traditional lending, while lending digital assets to earn interest.
1. Digital Currency:
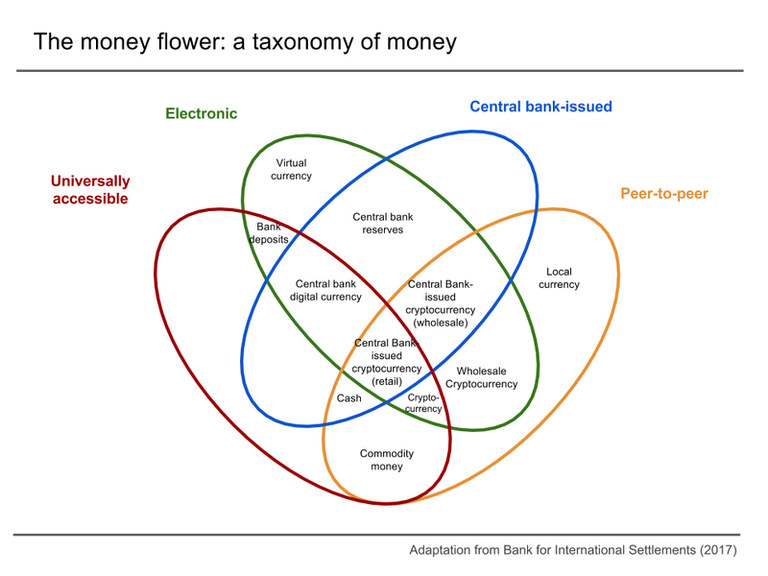
- Cryptocurrencies: Digital or virtual currencies secured by cryptography, operating independently of a central bank. Examples include Bitcoin and Ethereum.
- Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): A digital form of a country's fiat currency, issued and backed by the central bank. Unlike commercial bank balances, a CBDC represents a direct liability of the central bank.
- Existing Digital Money: Americans already use digital money in bank accounts and payment apps, but this is distinct from a CBDC because it's a liability of a commercial bank, not the central bank.
2. Digital Lending:
- Crypto Lending (Borrowing): Using your cryptocurrency as collateral to take out a loan.
- How it Works: You pledge your crypto holdings to a platform, which provides you with cash. You retain ownership of the crypto while repaying the loan.
- Risks: Failure to repay can result in the loss of your collateral. The value of your crypto can drop, potentially triggering a margin call.
- Crypto Lending (Lending out Digital Assets): You can lend your digital assets to platforms and earn interest on them.
- Digital Lending platforms: These platforms offer loans through websites and mobile apps, eliminating physical paperwork and paperwork.
- Technologies: They leverage cloud computing for infrastructure, robotic process automation (RPA) for tasks, and digital identity verification to streamline the process and improve security.